Infectious disease
Lyme borreliosis (or Lyme disease)
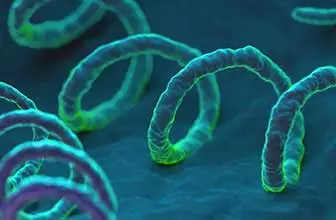
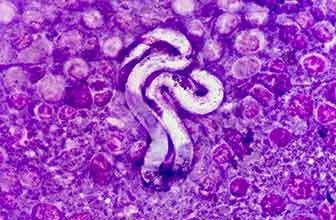
Lyme borreliosis, or Lyme disease, is a multisystemic vector-borne disease caused by bacteria of the genus Borrelia, being the most relevant Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii. Borreliosis is transmitted through tick bites, although it can also be transmitted by infected mosquitoes, fleas, or other insects. It affects humans and animals, mainly dogs, horses, and occasionally cattle. The main reservoirs for this spirochete are the white-footed mouse and the white-tailed deer. The most common symptoms are skin rash, fever, headache, and fatigue. If the disease is not treated or recognized early, more severe symptoms can develop and spread to the joints, heart, and nervous system. The treatment consists of antibiotics, which completely cure the disease if treated in time, and as a prevention it is recommended to avoid endemic areas and use insect repellents. The diagnosis of Lyme disease is complicated, since it has symptoms common to other diseases. Diagnostic tests usually help detect the disease, being the most common those that detect specific antibodies against the bacteria.
Lyme disease is a zoonoses with a worldwide distribution. It was discovered in the 1970s, and until two decades ago it only affected the northernmost part of the United States. Climate change and globalization have caused it to spread throughout the world: half a million people are diagnosed annually. The most prone areas are the United States, Europe and Asia. It is one of the world's most common tick-borne diseases for dogs, but only causes symptoms in 5-10% of infected dogs.
References of Lyme borreliosis (or Lyme disease)
RECOMBINANT ANTIGENS
Name, references, and description
ospC
- RAG0042 (B. afzelii)
- RAG0043 (B. burgdorferi)
- RAG0034 (B. garinii)
- Outer membrane antigen
VlsE
- RAG0022 (B. garinii, quimera)
- RAG0102 (B. afzelii)
- RAG0027 (B. burgdorferi, quimera)
- Major variable Surface antigen
flagellin B
- RAG0054 (B. afzelii)
- RAG0055 (B. burgdorferi)
- RAG0072 (B. garinii)
- Internal central portion of 41 kDa flagelline B protein (p41)
Brochures
- Rekom Biotech catalogue
- Recombinant proteins for in vitro diagnosis of human infectious diseases
- Recombinant proteins for in vitro diagnosis of animal infectious diseases
- Farm animal infectious diseases
- Recombinant proteins for vector-borne diseases
- Recombinant antigens for diagnosis of Lyme
Videos
Specialists in IVD reagents for infectious disease diagnosis
We ensure a commitment to absolute confidentiality regarding all information received and generated related to your project.
-
[[carrito.product.name]]
- [[sku.sku]]
Or if you prefer...
We will analyze your request to prepare a quote tailored to your needs.
-
[[carrito.product.name]]
- [[sku.sku]]
As manufacturers, we can adapt our products to your needs.
Contact us!